A scheme of arrangement under Part 26 of the Companies Act 2006 is a court-driven process that permits a restructuring on the basis that the requisite majority, by number and value, of the insolvent company’s creditors (or any class of them) vote in favour of it. Where there are different classes of creditors, the company will have to identify these classes in its first application to court seeking permission to convene and hold the meetings. The results of the voting at the statutory creditors’ meetings have to be formally reported to the court at a final hearing seeking the court’s order sanctioning the scheme. Continue reading “Schemes of arrangement of overseas companies”
Immigration appeals: the demise of the independent adjudicator
For some time, individuals making immigration applications both in the UK and outside of the UK have had the right to appeal to the Immigration Tribunal if their applications were refused. The statutory right to appeal, as set out in s82 of the Nationality, Immigration and Asylum Act 2002 (the 2002 Act), confirms that the following immigration decisions can be appealed:
Continue reading “Immigration appeals: the demise of the independent adjudicator”
Condition precedents: why, when and how should you use them?
When drafting a commercial agreement, it is prudent to think carefully about the potential issues that may lie ahead once the agreement has been signed and governs your commercial relationship with another party. In particular, where a certain event may trigger an onerous obligation on your part, you should think about whether the clause requires the protection of a condition precedent. Continue reading “Condition precedents: why, when and how should you use them? ”
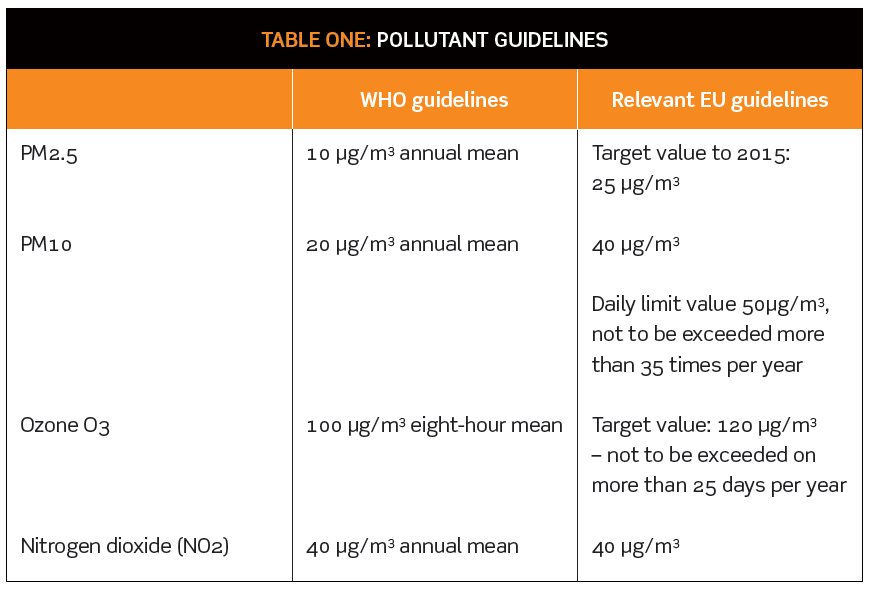
Failing health: why air quality legislation is not working
A whole body of well-established legislation controlling air pollution is failing to deliver results, in terms of preventing or reducing an estimated 29,000 premature deaths per year in the UK alone. The European Commission estimates that currently around 400,000 people die prematurely from outdoor air pollution across Europe. This article considers where and why the regulation of air quality is missing this health target. It attempts to give pointers to areas of future regulation. Continue reading “Failing health: why air quality legislation is not working ”
What is your ‘purpose’?
In a contractual dispute involving a written agreement, parties can face difficulties in proving the effect they originally intended particular words of the agreement to have, perhaps because the wording is ambiguous or fails to adequately express the intention of the contracting parties. In such circumstances, the court will analyse the agreement and the intention of the parties to determine the meaning of a particular word or clause, and consequently its legal effect. The existing case law is clear that this is an objective assessment, designed to establish what a reasonable person in the position of the parties would have understood the words in question to mean. This was concisely put by Lord Hoffmann in Investors Compensation Scheme Ltd v West Bromwich Building Society [1997]:
Sanctions: any relief?
The Jackson reforms, effective from 1 April 2013, brought about a number of significant changes to the Civil Procedure Rules (CPR), perhaps the most fundamental of which was the amendment of the overriding objective at CPR 1.1(1). Prior to amendment, Rule 1.1(1) stated that the CPR were designed to enable the court to deal with cases justly. By Rule 1.2 the court was required to effectuate the overriding objective when applying and interpreting the CPR. The new overriding objective requires the courts to deal with cases ‘justly and at proportionate cost’. Alongside this is a new sub-clause at Rule 1.1(2)(f) specifying that dealing with a case justly and at proportionate cost includes, so far as is practicable, ‘enforcing compliance with rules, practice directions and orders’. The effect of CPR 1.2 (above) is that this latter consideration now permeates and influences every case management decision taken under the CPR. Continue reading “Sanctions: any relief?”
England v Scotland: the difference on divorce and cohabitation
People largely associate forum shopping in divorces with crossing foreign borders, rather than moving within the UK. The reality, however, is that the Scottish laws regulating financial provision upon divorce are very different from those in England. In many cases this difference has little impact on the eventual outcome. However, in 5-10% of cases the financial outcomes on divorce will be substantially different, depending on whether the divorce is under English or Scots law. Continue reading “England v Scotland: the difference on divorce and cohabitation”
A review of the recent changes to UK immigration law and sponsorship
In the run up to the next general election on 7 May 2015, the UK government is implementing a raft of measures intended to reduce ‘illegal’ immigration in the UK. The latest of these measures is the Immigration Act 2014 (the Act), which received royal assent on 14 May 2014. The first element of this was implemented on 16 May 2014, in the form of a new code of practice on preventing illegal working. Continue reading “A review of the recent changes to UK immigration law and sponsorship”
Is alternative dispute resolution taking centre stage?
In the words of Mark Twain, there are ‘lies, damn lies and statistics’. It does seem, however, that whichever way you look at the latest figures detailed in the Civil Law Statistics for Scotland for the year 2012/13, there is an ongoing trend for individuals and businesses to rely less upon the Scottish court system for resolving their disputes. Continue reading “Is alternative dispute resolution taking centre stage?”
Sailing on the seven seas: international product liability perils
Today’s global economy presents both commercial opportunity and legal risk to producers. The vast majority of companies now trade on an international scale with design, manufacturing and distribution spanning the entire globe. However, international trade is not without risk where product liability is concerned. In this article, John Reynolds of Shook, Hardy & Bacon considers some of these risks and ways in which companies may limit exposure. Continue reading “Sailing on the seven seas: international product liability perils ”
Rent in administration proceedings: the Court of Appeal decision in Re Game Station
For a long time the issue of rent payable by a corporate tenant in administration appeared to be settled1. Landlords were apparently content to accept that, when a tenant company went into administration, the rent owing under the lease at the date of the administration was an ordinary unsecured claim. For the period of the administrators’ occupation and use of the premises they would pay the rent reserved by the lease apportioned on a daily basis as an expense in the administration. This established approach to rent in administration has come to be known as the ‘flexible’ or ‘pay as you go’ approach and was given judicial approval in the early 1990s in the leading case of Re Atlantic Computers Systems Plc (No 2) [1990]. Continue reading “Rent in administration proceedings: the Court of Appeal decision in Re Game Station”
Changes to codes of practice on prevention of illegal working
Two new codes of practice for employers came into effect on 16 May 2014, relating to the prevention of illegal working and avoiding unlawful discrimination in the legal right to work checking process. Continue reading “Changes to codes of practice on prevention of illegal working”