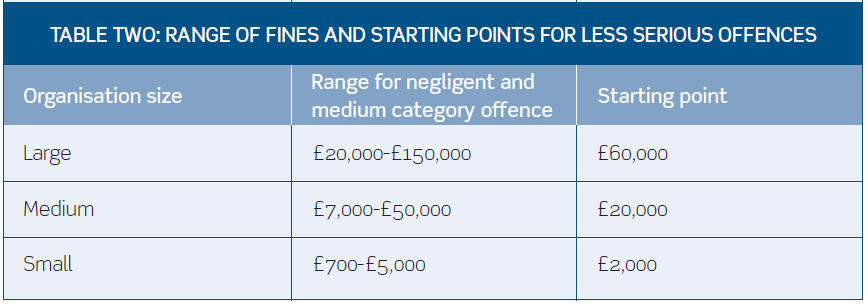
The Sentencing Council (the Council), an independent body that develops sentencing guidelines for the English courts, has just closed a consultation on proposals for new guidelines (the Guidelines) for the sentencing of environmental offences. There is no doubt that the Guidelines set out in the consultation, even if only partially implemented, will materially increase the level of fines for companies, businesses and individuals who breach environmental laws. This article examines the Guidelines and focuses on corporate penalties rather than individual offenders, although directors and officers of companies should be mindful that they can be liable for the same penalties as a company if it can be shown that the offence was committed with their consent, connivance or neglect. Continue reading “Paying for environmental incidents”
A healthy attitude to good faith
In the July 2012 edition of The In-House Lawyer, our colleagues discussed the importance of the first instance decision inCompass Group UK and Ireland Ltd (t/a Medirest) v Mid Essex Hospital Services NHS Trust [2012]. On 15 March, the Court of Appeal reversed Cranston J’s judgment. Continue reading “A healthy attitude to good faith”
Termination and disclaimer of contracts under Scots insolvency law
In the current economic climate, it is vital for in-house counsel to have a good understanding of both the powers that an organisation has to terminate contracts in the event that the other party to the contract enters insolvency, and the powers the insolvency practitioner (IP) enjoys in this regard.
Does insolvency have any automatic impact on the contract? Do the parties have any contractual rights to terminate the contract? Might the IP seek to disclaim the contract? If so, under what circumstances may this be done? Continue reading “Termination and disclaimer of contracts under Scots insolvency law”
Driverless vehicles: liability and new automotive technologies
The advance of GPS mapping, radar and wireless systems are making the ‘driverless car’ a possibility, sooner than many may have anticipated. The widely reported trials of an automated vehicle fleet utilising Google technology has raised the profile of automated vehicles significantly. Following these successful trials, the US states of Nevada, California and Florida have all passed laws permitting automated cars to drive on their roads.
Sarah Croft and John Reynolds, of Shook Hardy & Bacon International, assess the evolution of driverless or partially autonomous vehicle technology and consider the product liability issues arising for automotive manufacturers in the UK. Continue reading “Driverless vehicles: liability and new automotive technologies”
Are you obliged to act reasonably?
Commercial contracts often contain provisions that allow one party to take a certain step, or to make a particular decision, which will have an impact on another contracting party. Commenting on such a situation in Abu Dhabi National Tanker Co v Product Star Shipping Ltd (The ‘Product Star’) [1993], Leggatt LJ said that ‘where A and B contract with each other to confer a discretion on A, that does not render B subject to A’s uninhibited whim.’ In other words, the court will normally imply a term limiting the decision maker’s discretion. Continue reading “Are you obliged to act reasonably?”
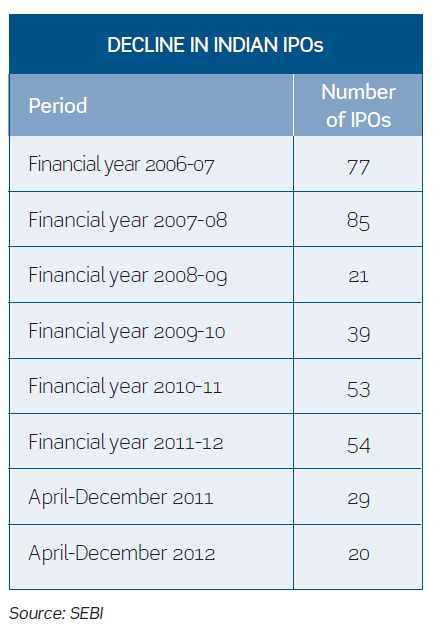
SEBI’s mandatory safety net mechanism
‘The dangers of life are infinite, and among them is safety’ – Goethe.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) issued a discussion paper on the ‘mandatory safety net mechanism’ in September 2012 (the SEBI discussion paper), inviting public comments. Briefly, this contemplates a mechanism wherein, in the event of a fall in share price within a specified period subsequent to listing, retail investors are able to tender back their shares purchased in an initial public offering (IPO), at the issue price, to the designated safety net provider. Continue reading “SEBI’s mandatory safety net mechanism”
Highly valued migrants: overview of the categories
The UK government has recently split up the UK Border Agency into two entities, namely the Immigration and Visa Directorate and the Immigration Law Enforcement Directorate, both of which will report directly to the Home Office.
The Tier 1 category of the points-based system1 was designed to allow highly talented migrants from outside Europe, and investors willing to invest a significant amount of capital, to enter the UK. Continue reading “Highly valued migrants: overview of the categories”
Sanctions and export controls: ignorance is not bliss
Over recent months, international sanctions and export controls have featured heavily in the news; the recent escalation of tension in the Korean peninsula, the ongoing conflict in Syria and Iran’s continued attempts to develop nuclear weapons are all examples of international situations where sanctions or trade controls are in force. Even though these are examples that attract headlines, there are multiple pitfalls in other less high-profile countries and industries in which an unaware company can slip up and which can result in serious implications for the company and the individuals involved. It therefore seems like a sensible time to provide an introduction to those unfamiliar with the area as well as identify key areas of potential concern for those in an in-house/compliance role. Continue reading “Sanctions and export controls: ignorance is not bliss ”
Information exchange: don’t slip on the banana skin
Two recent judgments of the General Court of the EU (the Court)1 provide a stark reminder of the long reach of competition law in relation to exchanges of information between competitors. Although the European Commission’s findings of fact in these cases disclosed a frequent and detailed series of communications concerning future prices, it would be wrong to dismiss the relevance of the Court’s approach as concerning only situations of grave infringements. The reasoning and underlying policy of the Court (and of the Court of Justice of the EU) applies to a much broader category of situations, many of which may be uncomfortably close to the kind of discussions between competitors in trade associations and elsewhere that have not raised red flags. The Banana cases are a warning to companies to look to their industry and corporate practices to ensure that there are no information exchanges that might offend under this extended form of competition control. Continue reading “Information exchange: don’t slip on the banana skin”
Industrial heat use and the Heat Strategy
The issues of efficient heat and reducing emissions from the generation of heat are rapidly moving up the political agenda. Industry needs to watch these developments closely and be prepared. Six industry sectors, including chemicals, oil refining, food and drink, basic metals, pulp and paper and non-metallic minerals (including ceramics, cement and glass) are singled out as target sectors by the government’s heat strategy, The Future of Heating: Meeting the Challenge (the Heat Strategy) published in March 2013, but other industry sectors should also be concerned. Continue reading “Industrial heat use and the Heat Strategy”
A frustrating accident? Bunge SA v Kyla Shipping Co Ltd [2012]
The doctrine of frustration was developed in Taylor v Caldwell (1863). In that case, the plaintiff had agreed to hire a music hall for concerts on four specified evenings. A fire destroyed the music hall before the concerts took place. The plaintiff sought damages from the owner of the hall on the basis that he was in breach of his contractual obligation to make the hall available. The Court of Queen’s Bench rejected the claim on the basis that: Continue reading “A frustrating accident? Bunge SA v Kyla Shipping Co Ltd [2012]”
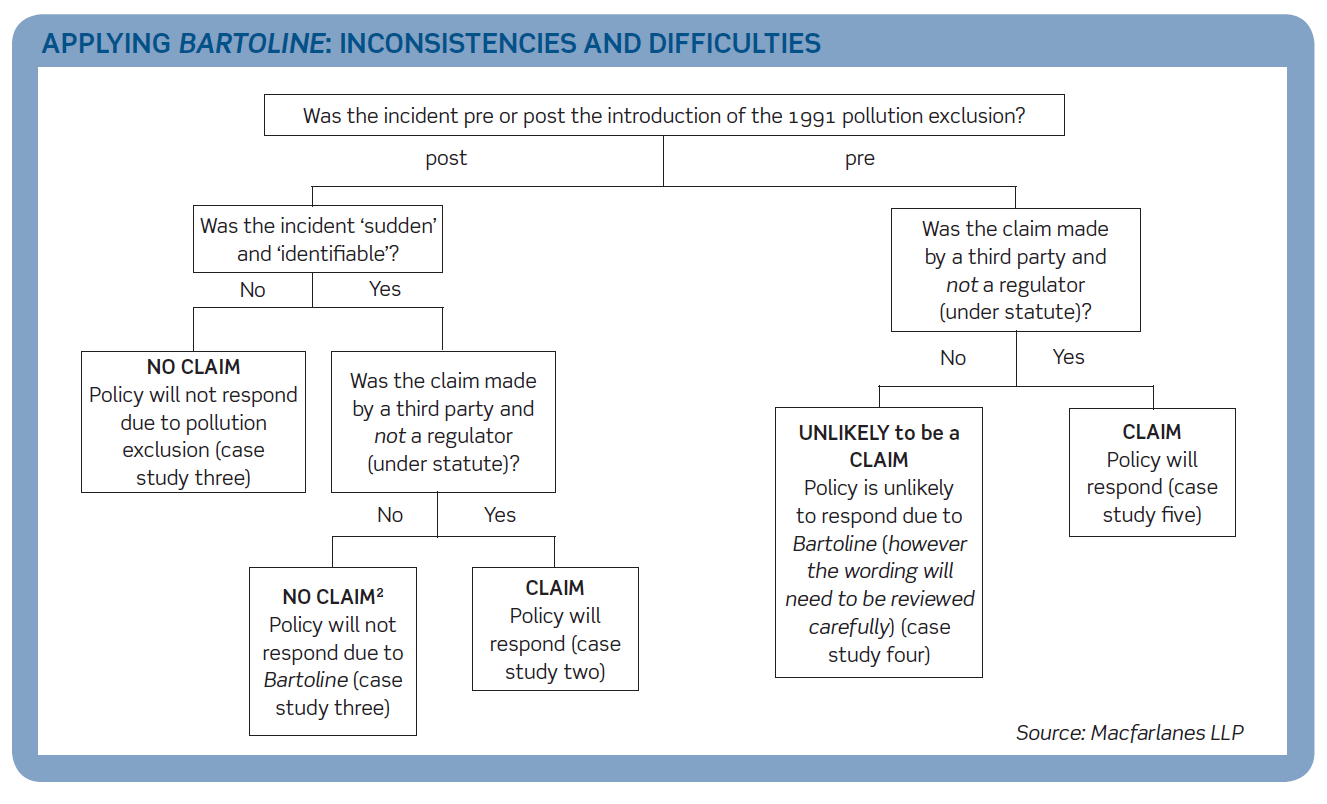
Revisiting Bartoline
The decision in Bartoline v Royal Sun Alliance [2006] has some commentators arguing that the door has effectively been shut on recovering environmental liabilities under public liability (PL) policies. This article examines whether this is true; it looks at the legal principles in Bartoline, its impact on the environmental insurance market and the likely future of the PL insurance market in the UK. Continue reading “Revisiting Bartoline”